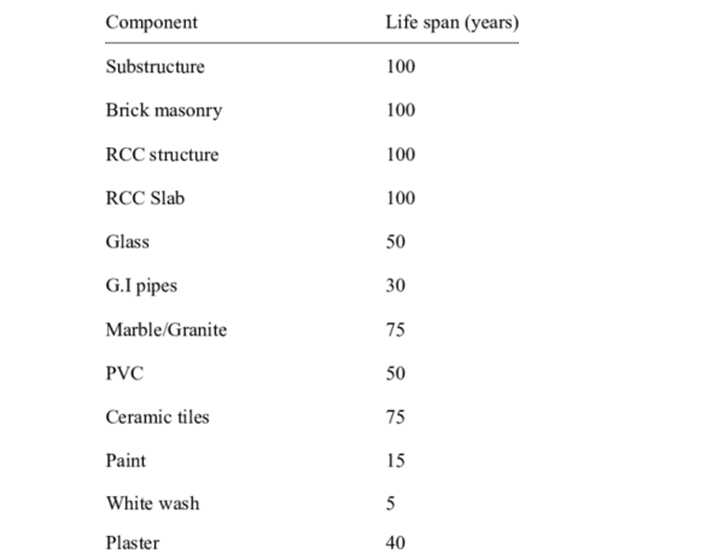
Structural Audit & NDT
As one of the leading structural audit consultants Mumbai MSC Project Consultants have done structural audit of more than 200 buildings in last 5 years. Real estate in the form of Residential Buildings, Commercial, Institutional or Industrial buildings are the most important assets of everyone’s lifetime.
Well, it depends on a lot of factors including external weather conditions and property and quality of building materials used.
If you are particular about concrete, creep plays a major role. The amount and strength of steel reinforcement and concrete are also very important. The corrosion of steel reinforcements drastically reduces the life span.
So without specifications & detailed Structural audit, it would be hard to give an estimate for a life span. But generally, the age is estimated as 65 to 70 years.
- Historical structures (temples, etc) – 500-1000 yrs
- Steel structures – 100-150yrs
- Concrete structures – 100yrs
- Personal or commercial bldgs – 60-80yrs
- Rigid roads – 30-35yrs
- Flexible roads – 8-10yrs
- Design Philosophy
- Type of material used in the structure
- Climate condition
- Location
- Repair and maintenance period
- earthquake zone etc
It is very obvious that we all need to starve hard to increase the ‘Life-Span’ of any Building or structure. The most important aspect of increasing the ‘Life-Span’ of any structure is to practice regular ‘Maintenance’. The scope of the maintenance is derived based on the Structural audits, which includes RCC, track & trace the Leakages/seepages, Plumbing, Electrical fittings, cable wirings & HVAC units. We at MSC PROJECT CONSULTANTS help our esteemed clients to perform following audits –
- Structural Audits
The following NDT tests are required to be carried out on structural elements. However, it is important that the testing scheme is prepared based on a preliminary survey of the building/ structure:
- Rebound Hammer Test
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Test
- Corrosion Test of Steel
- Carbonation Test
- Core Test
- Half-cell potentiometer Test

- Electrical Safety audits
Electrical Safety audits – Identification of electrical hazards and minimizing the risk of accidents like fires due to short-circuiting. Identification of areas of risk in your electrical systems. Non-compliance with the legislation and best practice.
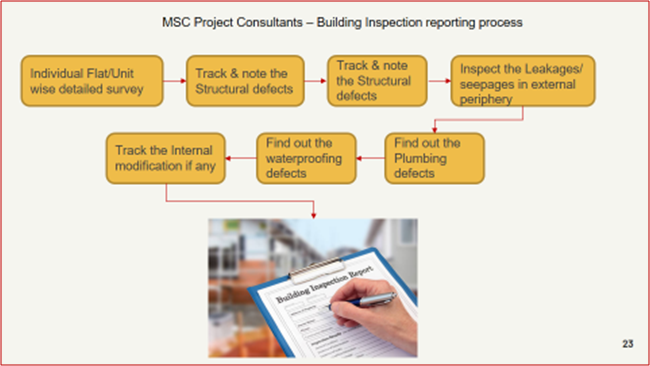
Building restoration survey process by MSC Project Consultants
We carry out a detailed internal and external survey to decide the priorities of various items like structural repairs, stopping leakages and seepages, aesthetics and general rehabilitation.
A budget estimate is then prepared using the BOQ, indicating the likely cost to be incurred under different heads and the cumulative cost. The committee needs these inputs to budget/funds through various accounts heads like building repairs funds, sinking fund etc. This budgeted estimate also helps to derive the exact ‘Scope of work’ (SOW)
Non-destructive testing (NDT)
Non-destructive testing is important for the Quality Assurance of hardened concrete and the evaluation of existing concrete structures with regard to their strength & durability.
Types of Non Destructive Testing
Following are the commonly done Non-Destructive Tests for concrete:
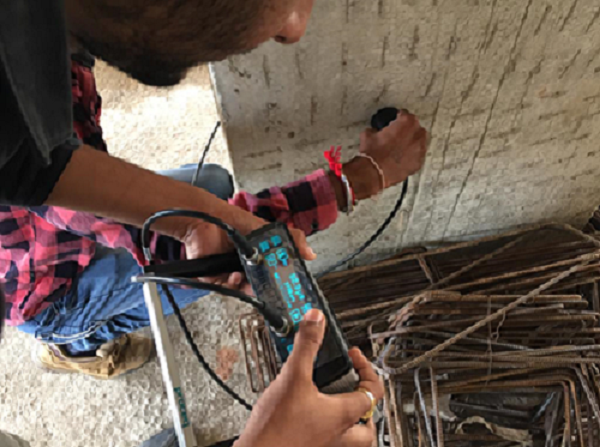

Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Testing:
This test is done to assess the quality of concrete. The method consists of measuring the time of travel of an ultrasonic pulse passing through the concrete being tested. Comparatively higher velocity is obtained when concrete quality is good in terms of density, uniformity, homogeneity, etc.
Rebound Hammer Test:
Rebound Hammer test is a Non-destructive testing method of concrete which provide a convenient and rapid indication of the compressive strength of the concrete. The rebound hammer is also called as Schmidt hammer. It consist of a spring-controlled mass that slides on a plunger within a tubular housing. When the plunger of the rebound hammer is pressed against the surface of the concrete, a spring-controlled mass with constant energy is made to hit the concrete surface to rebound back. The extent of rebound, which is a measure of surface hardness, is measured on a graduated scale. This measured value is designated as Rebound Number (rebound index). A Concrete with low strength and low stiffness will absorb more energy to yield a lower rebound value.

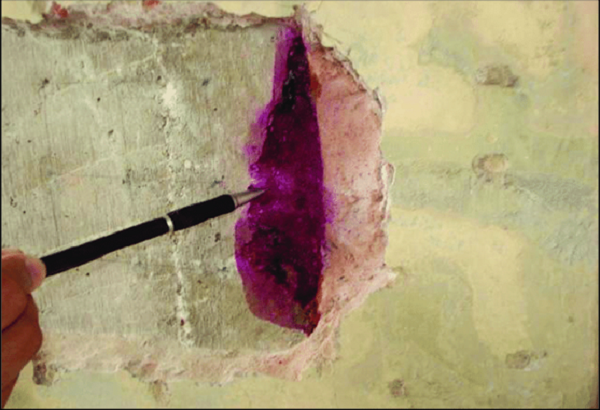
Carbonation:
Carbonation occurs in concrete because the calcium-bearing phases present are attacked by carbon dioxide in the air and converted to calcium carbonate. Depth of Carbonation is assessed using a solution of phenolphthalein indicator that appears pink in contact with alkaline concrete with pH values in excess of 9 and colorless at lower levels of pH.
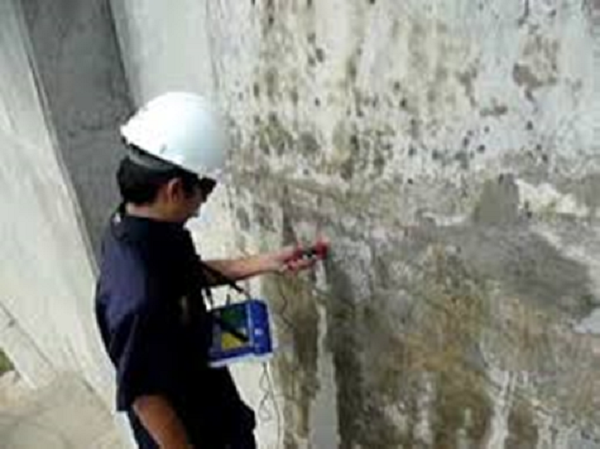
Half Cell Potential: -200 mv less negative than 200 mv:
This test provides an indicator of the level of corrosion or the corrosive potential within the concrete. The test is used extensively for condition surveys of suspect RCC structures to identify areas with corrosion activity for further analysis to establish the cause of corrosion and estimate residual service life.


Concrete Core Testing:
Carbonation occurs in concrete because the calcium-bearing phases present are attacked by carbon dioxide in the air and converted to calcium carbonate. Depth of Carbonation is assessed using a solution of phenolphthalein indicator that appears pink in contact with alkaline concrete with pH values in excess of 9 and colorless at lower levels of pH.
Chemical Testing of Concrete:
Chemical analysis of concrete is done to determine the pH value, chlorides, sulphates etc. to understand the causes of failure of concrete. Whenever there is chloride in concrete, the risk of corrosion increases with warm, moist conditions. The chloride content should not be more than 0.6 Kg/Cu.M of concrete. Sulphates present in the concrete can cause expansion and disruption of concrete. The total water-soluble sulphate content of the concrete mix expressed as SOl’ should not exceed 4 percent by mass of the cement in the mix.


Some of the main reasons of building collapse are as follows
- Bad design.
- Faulty construction.
- Extraordinary loads.
- Foundation failure.
- Unexpected failure mode.
- Natural disasters.
- Soil liquefaction.
- Demolition through explosives.
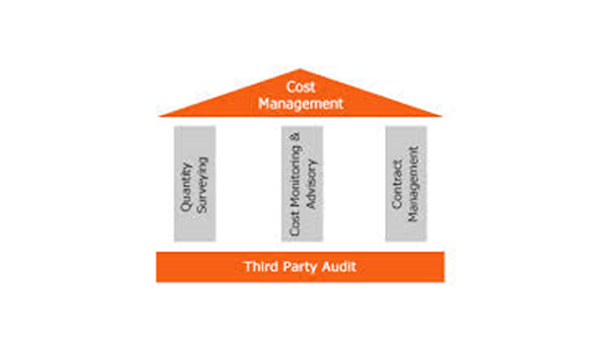
Management and quantity surveying (QS)
We offer services on a vast range of construction projects, including buildings, civil engineering, industrial & infrastructure. The firm’s QS specialists are an integral part of the design and project management team on projects of all sizes and levels of complexity.
What sets MSC PROJECT CONSULTANTS apart is that its cost managers and quantity surveyors are fully integrated into the engineering environment to provide an effective means of achieving the client’s objectives. They contribute to projects with in-depth knowledge of built environment design and the concerns of designers and clients. They share the firm’s commitment to sustainable development, project performance, and life-cycle analysis.
Cost control and value management
Cost planning and value management include the evaluation of alternative designs against the client’s value criteria for function, quality, and durability. The evaluation techniques enable the design team to optimize the design to fit within the client’s budget.
Cost control is achieved through formal change control procedures and regular cost reporting. This is designed to give up-to-date cost information to the client and the designers and to provide a full audit trail of changes against an approved budget.
Procurement, tendering and contract administration
MSC PROJECT CONSULTANTS’s project and cost management team includes experienced quantity surveyors based around the world. Their services range from project conception to design development and include advice on procurement and tendering methodologies, management of the procurement process from tenderer selection through tender evaluation to contract award, and post-contract administration, leading to the agreement of the final account, including the resolution of potential contractual disputes.
Knowledge sharing through the firm’s internal networks allows resources and experience to be drawn from many locations around the firm to support and supplement core teams.

